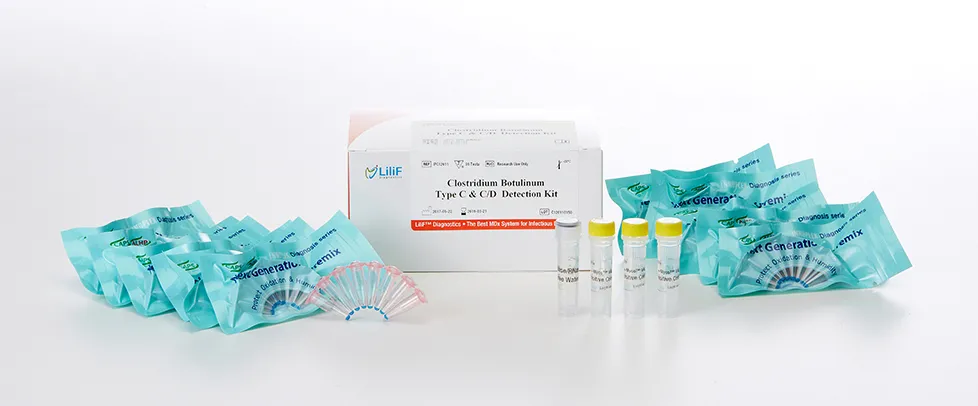
LiliF® CB type C & C/D PCR Kit
Background Information
Clostridium botulinum is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, anaerobic, spore-forming, motile bacterium with the ability to produce the neurotoxin botulinum. The botulinum toxin can cause a severe flaccid paralytic disease in humans and other animals and is the most potent toxin known to mankind, natural or synthetic, with a lethal dose of 1.3–2.1 ng/kg in humans. Most strains produce one type of neurotoxin, but strains producing multiple toxins have been described. C. botulinum producing B and F toxin types have been isolated from human botulism cases in New Mexico and California. The toxin type has been designated Bf as the type B toxin was found in excess to the type F. Similarly, strains producing Ab and Af toxins have been reported. Evidence indicates the neurotoxin genes have been the subject of horizontal gene transfer, possibly from a viral source. This theory is supported by the presence of integration sites flanking the toxin in some strains of C. botulinum. However, these integrations sites are degraded, indicating that the C. botulinum acquired the toxin genes quite far in the evolutionary past. Only botulinum toxin types A, B, E, F and H cause disease in humans. Types A, B, and E are associated with food-borne illness, with type E specifically associated with fish products. Type C produces limber-neck in birds and type D causes botulism in other mammals. No disease is associated with type G. The "gold standard" for determining toxin type is a mouse bioassay, but the genes for types A, B, E, and F can now be readily differentiated using quantitative PCR. As no antitoxin to type H is yet available, discovered in 2013 and by far the deadliest, details are kept under shroud. A few strains from organisms genetically identified as other Clostridium species have caused human botulism: C. butyricum has produced type E toxin and C. baratii had produced type F toxin. The ability of C. botulinum to naturally transfer neurotoxin genes to other clostridia is concerning, especially in the food industry, where preservation systems are designed to destroy or inhibit only C. botulinum but not other Clostridium species.
LiliF™ CB type C & C/D PCR Kit is able to detect directly and specifically CB by CLP™ technology and Maxime™ technology on the basis of a genetic database of target nucleic acid fragments. Therefore, this kit can diagnose very sensitive, fast and accurately. The kit contains a specific primer set for a highly conserved region based on current sequence alignments of toxin gene of C. botulinum serotype C and C/D, allowing the DNA detection. It can determine the infecting all serotype and accurately and sensitively detect multiple detection genes at one time using the conventional PCR method, and take only 2 hours for detection. Fast and sensitive detection of pathogen enables patients to get appropriate treatment and prevent the rapid spreading of disease by separating patients immediately.
Principle
• This product is a qualitative PCR testing product with CLP™ technology which provided flexibility in Tm (melting temperature) of primer design for optimization of reaction condition, and maximizes PCR specificity and sensitivity through the control of non-specific priming.
• The assay is a PCR that discriminates Clostridium botulinum serotype C, C/D in one reaction. The assay is composed of two principal steps: (1) nucleic acid extraction from specimens, and (2) amplification of the target extracted nucleic acid fragment using specific primers pair.
Intended Use
• For Research Use Only, Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
• This kit is developed, designed, and sold for research purpose only. It is not intended to be used for human or animal diagnosis of diseases. Prior to using it for other purposes, the user must validate the system in compliance with the applicable law, directives, and regulations.
• This product is research reagent of infectious disease for professional use to restrict the public use for animal diseases.
- Categories : PCR Kits, Diagnostic Use, Animal Diagnostics
.webp)
(1).webp)
(2).webp)
(3).webp)
(4).webp)
(5).webp)
(6).webp)
(7).webp)
(8).webp)
(9).webp)
(10).webp)
(11).webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)